
Ours future directions are to investigate CAF-1 interaction networks to understand its function in chromatin assembly and in maintaining genome stability at DNA repair/replication stress sites, in yeast and humans. XThe team has revealed novel functions of CAF-1 in promoting HR-dependent events at stressed forks by stabilizing D-loop intermediates and counteracting D-loop disassembly by the helicase Rqh1-mediated. The Chromatin Assembly Factor 1 (CAF-1) promotes the direct deposition of H3-H4 in a manner coupled to DNA synthesis. If replication fork regression occurs only upon blockage of a fork and disengagement of the replication enzymes from the fork, then the frequency of fork regression will be determined, at least in part, by the frequency of blockage and the stability of replisome association with a blocked fork.

At replication forks, several histone chaperones are at work to regulate histones flux. The number of replication forks that are present in a cell depends on the type of DNA replication that is occurring. In this process, the standard three-way junction forks are converted into four-way junction structures. Histones deposition on DNA is facilitated by a family of proteins called histone chaperones. Replication Fork Reversal and its Players Remodeling of RFs involves unwinding of newly synthesized strands and annealing of nascent and parental strands. Genomes are routinely exposed to a variety of DNA damages that induce profound chromatin rearrangements and pose serious threat to epi-genome integrity during DNA replication.ĭespite the recent identification of chromatin restoration pathways upon DNA repair, the crosstalk and coordination between both processes, that is likely key to safeguard genome integrity, remain poorly understood. Replication fork processing that includes recombination between DNA near the arrested fork and homologous sequences.
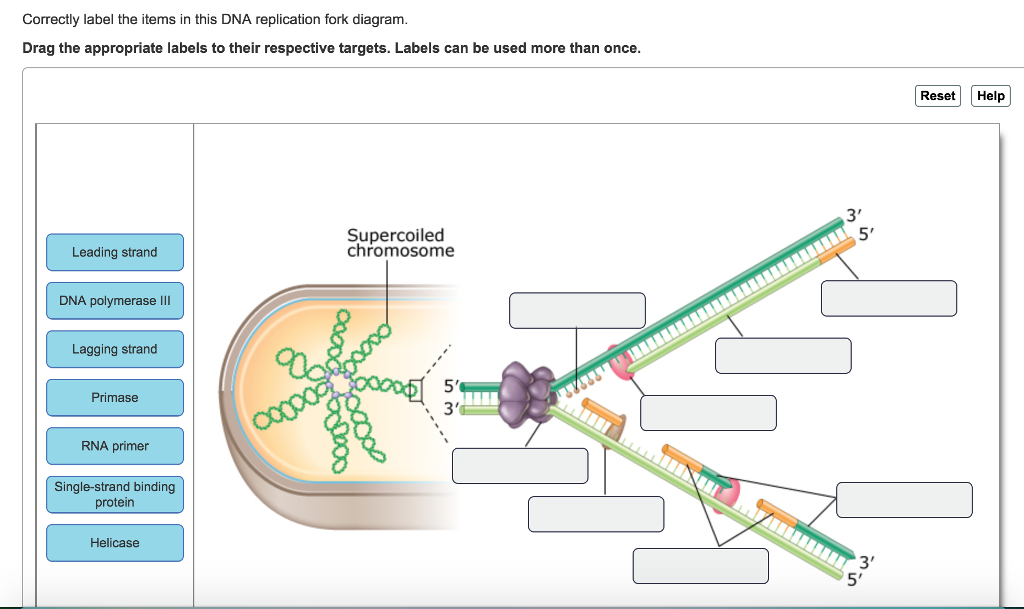
DNA replication fork arrest during DNA-dependent DNA replication is not known to occur outside of cases where a replication error needs to be prevented or corrected.
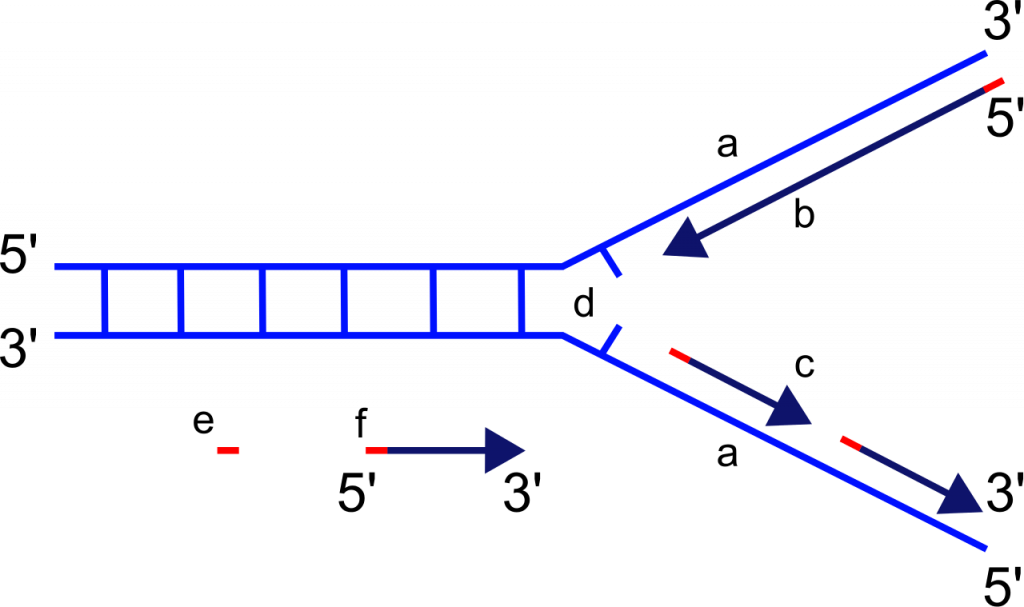
Chromatin constitutes a barrier to DNA replication and repair machineries that should be first lifted and then restored behind the replication fork or once the repair event is achieved. Replication fork arrest is one of the quality control processes ensuring that DNA-dependent DNA replication occurs correctly. The maintenance of genome integrity occurs in the context of DNA packaged into chromatin.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
